Prof. Dr. Goutam Guha (M.S., M.Ch)
Consultant Plastic, Cosmetic and Reconstructive Surgeon.

Consultant Plastic, Cosmetic and Reconstructive Surgeon.

Cosmetic Breast Surgery (Female)
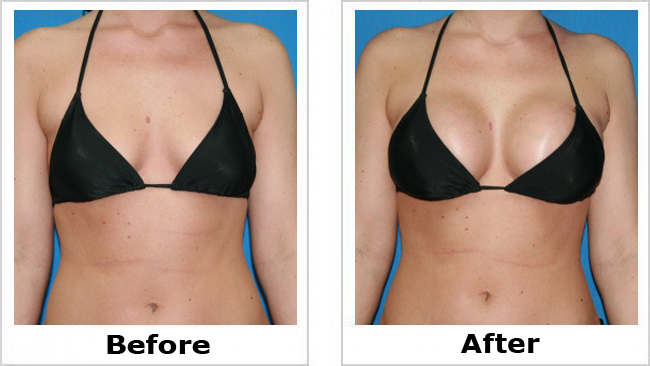
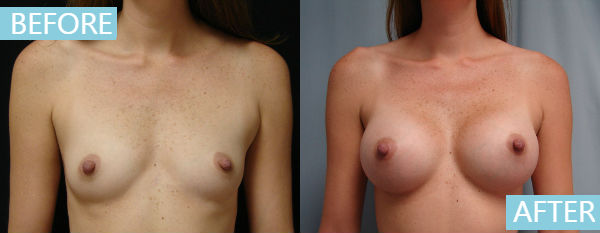
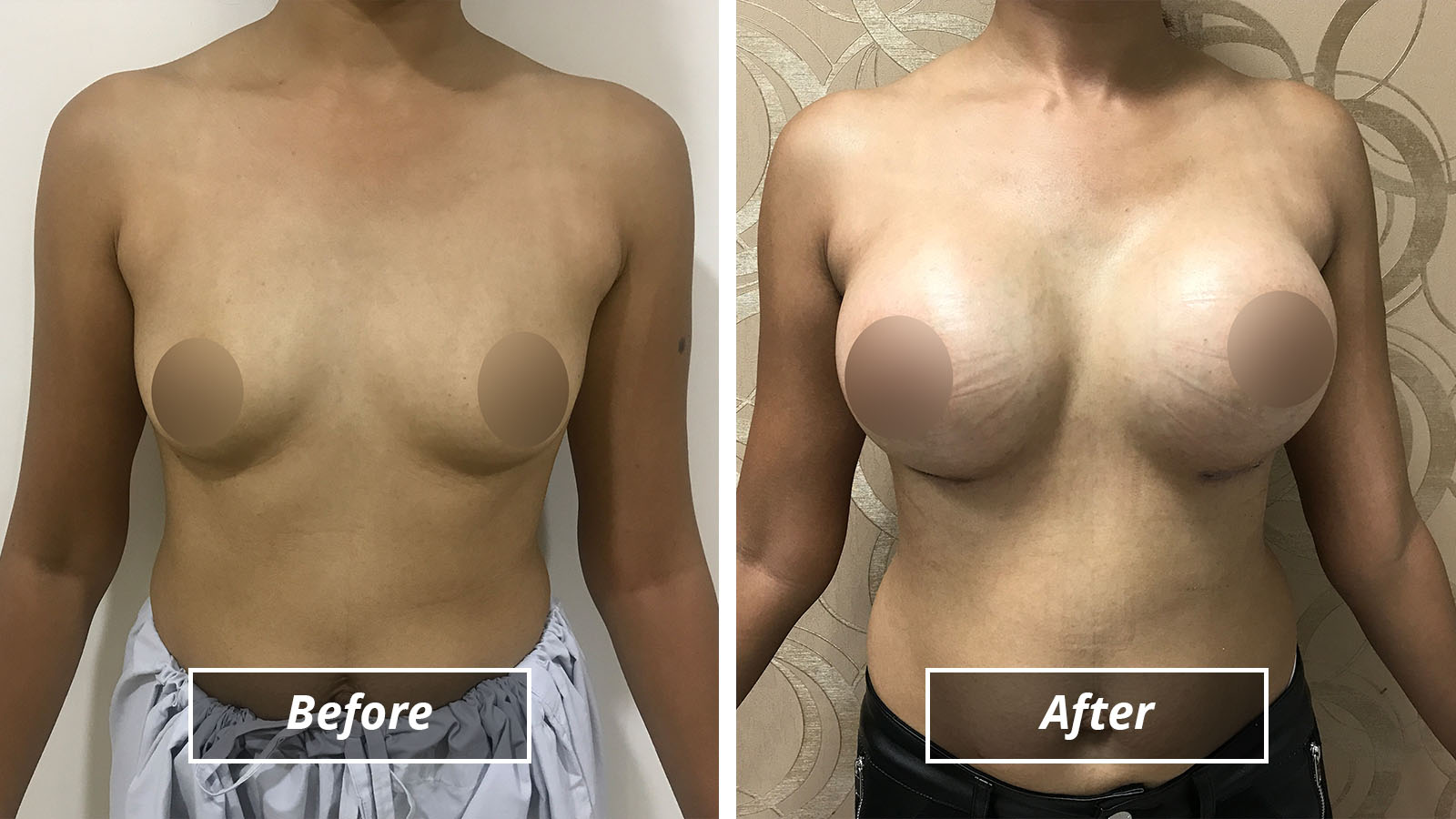
Breast Augmentation1) Breast Augmentation -
Breast augmentation surgery increases or restores breast size using silicone gel implants, saline implants or in some cases, fat transfer. One of the most popular and frequently performed aesthetic surgery procedures, breast augmentation has a long and successful track record in satisfying women who wish to enhance, regain or restore balance to their figures.
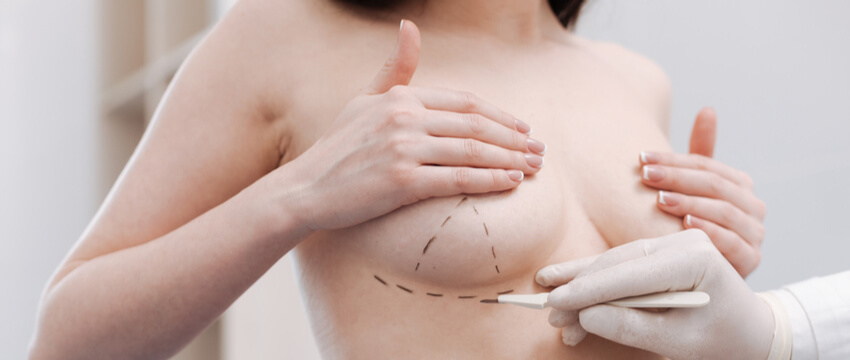
When to Consider Breast Augmentation
. You believe your breasts are too small for your body.
. You feel self-conscious wearing a swimsuit or form-fitting or low-cut tops.
. Clothes that fit your hips are too large at the bust line.
. Your breasts have become smaller or less firm after you've had children.
. Your breasts have become smaller due to weight loss.
. One of your breasts is noticeably smaller than the other.

Limitations and Risks
Fortunately, significant complications from breast augmentation are infrequent. Your specific risks for breast augmentation will be discussed during your consultation.
All surgical procedures have some degree of risk. Some of the potential complications of all surgeries are:
. Adverse reaction to anesthesia
. Hematoma or seroma (an accumulation of blood or fluid under the skin that may require removal)
. Infection and bleeding
. Changes in sensation
. Scarring
. Allergic reactions
. Damage to underlying structures
. Unsatisfactory results that may necessitate additional procedures
. All surgical procedures have some degree of risk. With breast augmentation, minor complications occur occasionally, but do not affect the outcome. Major breast augmentation complications are very unusual.
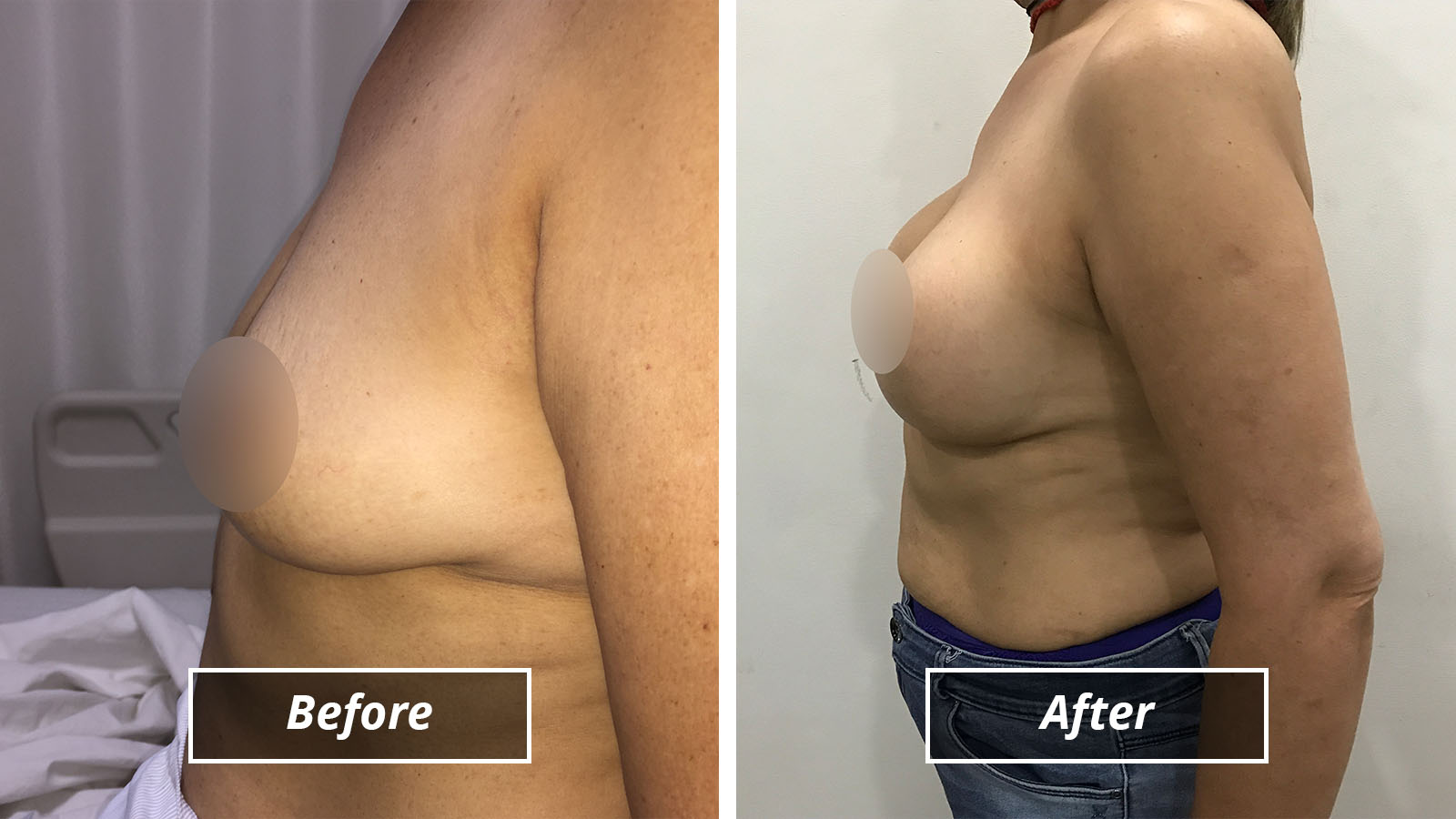

2) Breast Reduction -
The goal of breast reduction surgery is to reduce the size of your breasts and reshape them so that they are proportionate to the rest of your body and are no longer a source of physical discomfort. This commonly requested, predictable procedure has the dual benefits of improving your appearance while relieving the physical and emotional burden of overly large breasts.
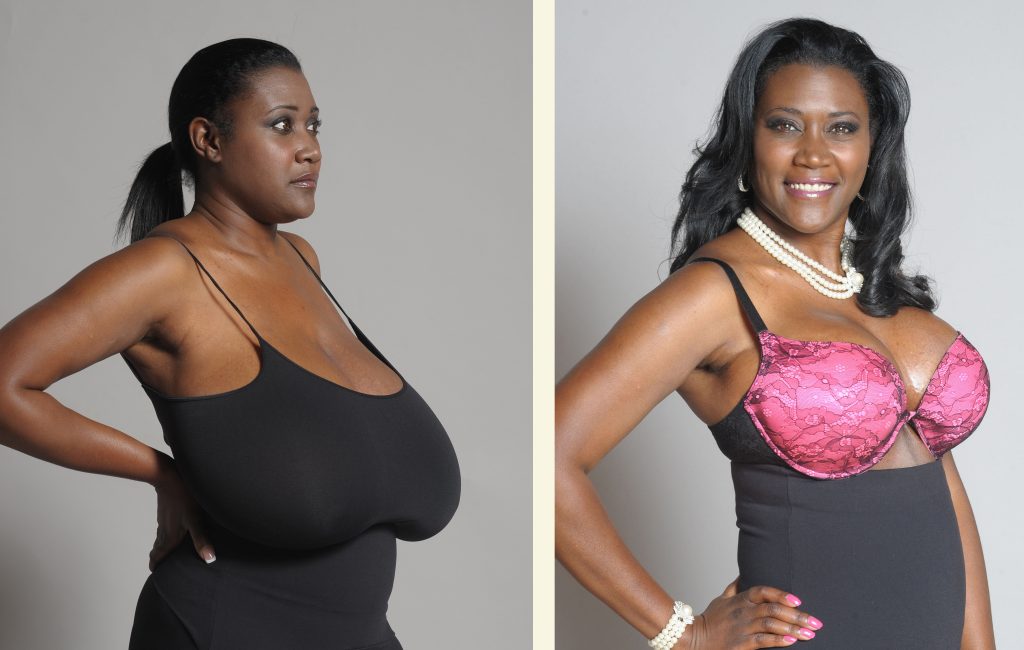

When to Consider Breast Reduction
. You have backaches, neck aches, or skin irritation under your breasts.
. You have difficulty breathing and notice grooves in your shoulders from your bra straps.
. You have poor posture or numbness in parts of your breasts and upper chest from excessive breast weight.
. You find it nearly impossible to buy dresses and blouses and difficult to find tops that fit.
. You are very unhappy with your appearance because of your breast size.
. You are in good health with no active diseases or pre-existing medical conditions.
. You have realistic expectations of the outcome of your surgery. You must be able to discuss what you want with your plastic surgeon so that you can reach an understanding of what can realistically be achieved.
. Your skin has adequate elasticity, so it can resume its former tightness following surgery.
. You are mentally and emotionally stable. Breast reduction requires patience and stability to deal with the healing period.
. You are old enough so that your breast development has stopped.
. You have finished having children and breast-feeding, because this can have significant and unpredictable effects on the size and shape of your breasts.

Limitations and Risks
Fortunately, serious risks of breast reduction surgeries are rare and the satisfaction rate with these procedures is high. The overall complication rate is small if the operation is done by an experienced plastic surgeon operating in an accredited facility.


All surgical procedures have some degree of risk. Some of the potential complications of all surgeries are:
. Adverse reaction to anesthesia
. Hematoma or seroma (an accumulation of blood or fluid under the skin that may require removal)
. Infection and bleeding
. Changes in skin sensation
. Scarring
. Allergic reactions
. Damage to underlying structures
. Unsatisfactory results that may necessitate additional procedures
. Blood clots in the legs or lungs
. You can help minimize certain risks by following the advice and instructions of your board-certified plastic surgeon, both before and after your breast reduction.
3) Mastopexy / Breast lift procedure -
Breast lift procedureA breast lift addresses sagging and uneven breasts, decreased breast volume and drooping nipples and stretched areolas (the darker area surrounding the nipples), recreating a youthful shape and lift to your breasts. If there is too little or too much breast volume, a breast augmentation or breast reduction might be recommended in addition to a lift. Every year, thousands of women undergo successful breast-lift surgery, experience no major problems and are pleased with the results.

When to Consider a Breast Lift
. Breasts that are pendulous but adequate in size. . Breasts that lack substance or firmness. . Nipples and areolas that point downward, especially if they are positioned below the breast crease. . Breasts that appear different from each other; one breast may appear firm and well positioned while the other does not. . Breasts that are not equal in size. . Breasts that are relatively small. . Breasts that are large and heavy can be lifted, but the results may not be as long-lasting as a breast lift performed on smaller breasts; the weight of larger breasts works against surgical changes. . You are finished with childbearing and breast-feeding. If you plan to have children, you may want to postpone cosmetic breast surgery. Pregnancy may stretch the breasts and reduce their volume, compromising surgery benefits.

Limitations and Risks
Fortunately, significant complications from breast lift are infrequent. Your specific risks for breast lift will be discussed during your consultation.
All surgical procedures have some degree of risk. Some of the potential complications of all surgeries are:
. Adverse reaction to anesthesia
. Hematoma or seroma (an accumulation of blood or fluid under the skin that may require removal)
. Infection and bleeding
. Changes in sensation
. Scarring
. Allergic reactions
. Damage to underlying structures
. Unsatisfactory results that may necessitate additional procedures
. Blood clots in the legs or lungs
Picture Gallery